How to work with CORS in Darklang
By default, browsers don't allow Javascript to make certain kinds of API calls to a different domain than the JS was loaded from. This is called the "same-origin policy", and it's used to protect users from having their credentials stolen by malicious web pages. The browser will check with the server to see if it's allowed make the request, based on the origin of where the JS application loaded.
To support intentional uses of APIs from different domains, browsers have all implemented CORS: "cross origin resource sharing". More general information on CORS is available in the Fetch standard, and in the MDN documentation.
This document addresses the common needs developers run into with respect to CORS when writing an application in Darklang. The three primary pieces of CORS this document addresses are:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin— what domains requests are coming from.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials— using tokens ("BearerAuth") or cookies within your application.Access-Control-Allow-Headers&Access-Control-Allow-Methods— specific methods & headers used within the application.
Out of the Box CORS Settings in Darklang
Darklang automatically uses permissive canvas-wide CORS settings with localhost to make it easy to get started when developing your backend with Darklang.
- Today, Darklang sets accepts requests from localhost:3000, localhost:5000, and localhost:8000, as long as you do not have special headers or authentication. More on the default supported headers is in MDN.
- In the future for any version of localhost, we will also return all headers from the preflight request, all common methods, and accept credentials. This work will also set max-age to something short to avoid caching issues. If this is blocking you, please let us know to help elevate the priority of this project.
Today, if you need authentication (including cookies) or special headers you will need to include CORS settings.
Simple Requests without Preflighting
Some simple requests do not require CORS preflighting. This may be the case if your request meets both of these requirements:
- Method: GET, HEAD, POST
- Content Type:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded,multipart/form-data, andtext/plain. - There are a couple other details, which you can check here: detailed explanation.
For simple requests, the CORS settings should be returned within the endpoint. Here is an example of setting the headers for simple request that requires an allowed list of origins:
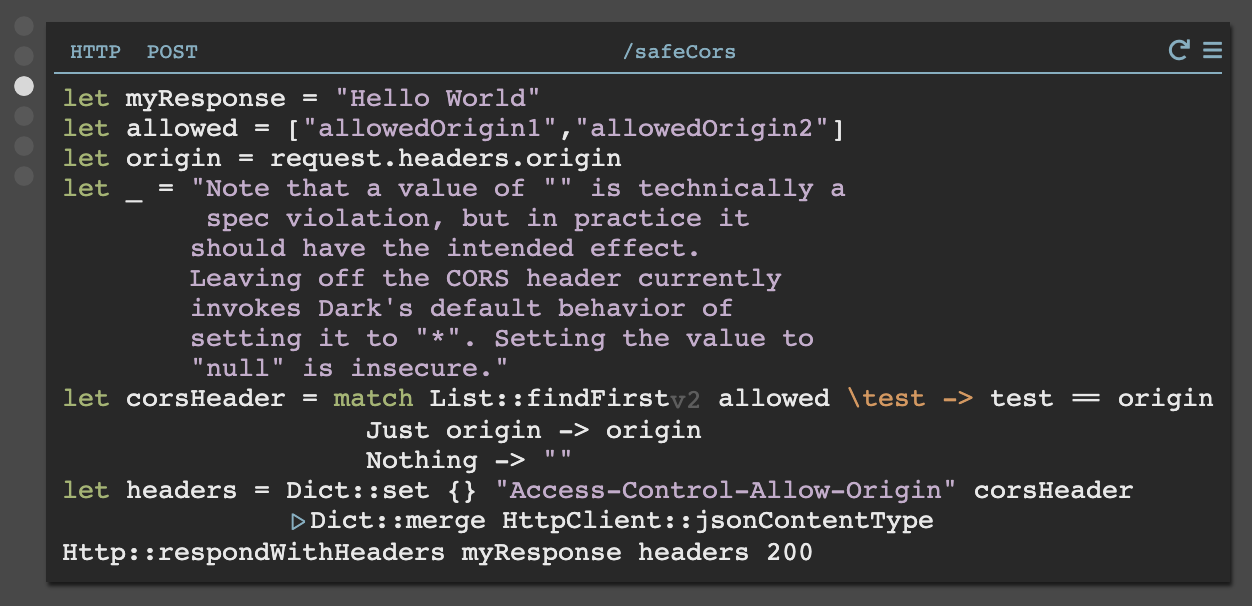
Adding Preflighting via OPTIONS Handlers
If you require another method, header, or credentials, the CORS preflight must be handled via an Options header. The browser will call the options header to get information, and then make its request accordingly.
Options Method
Options is not a default method on HTTP handlers, but can be entered.
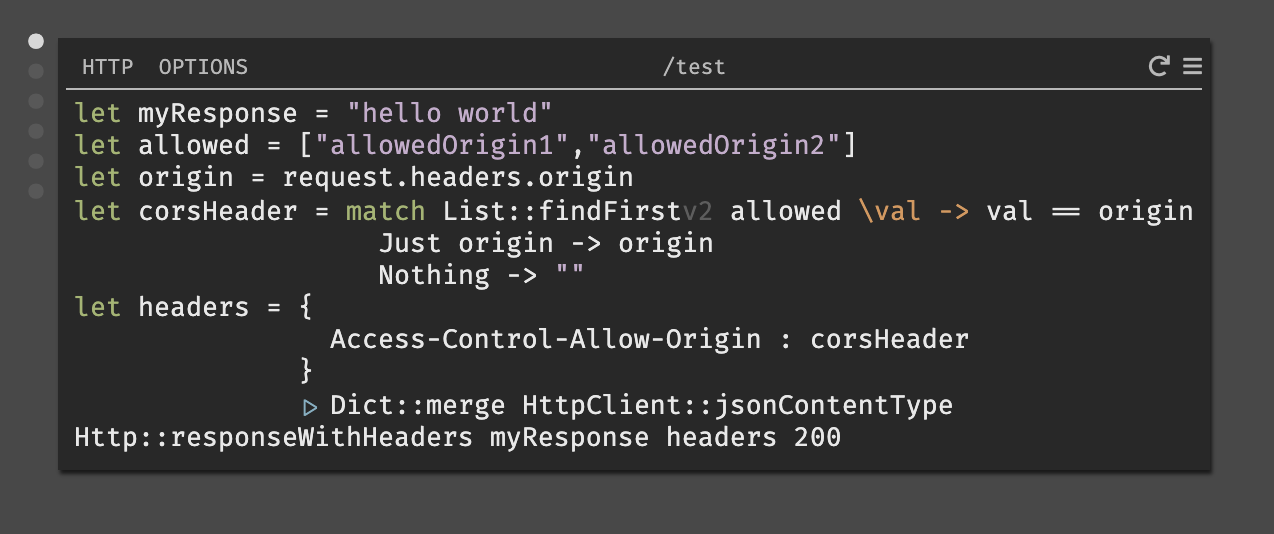
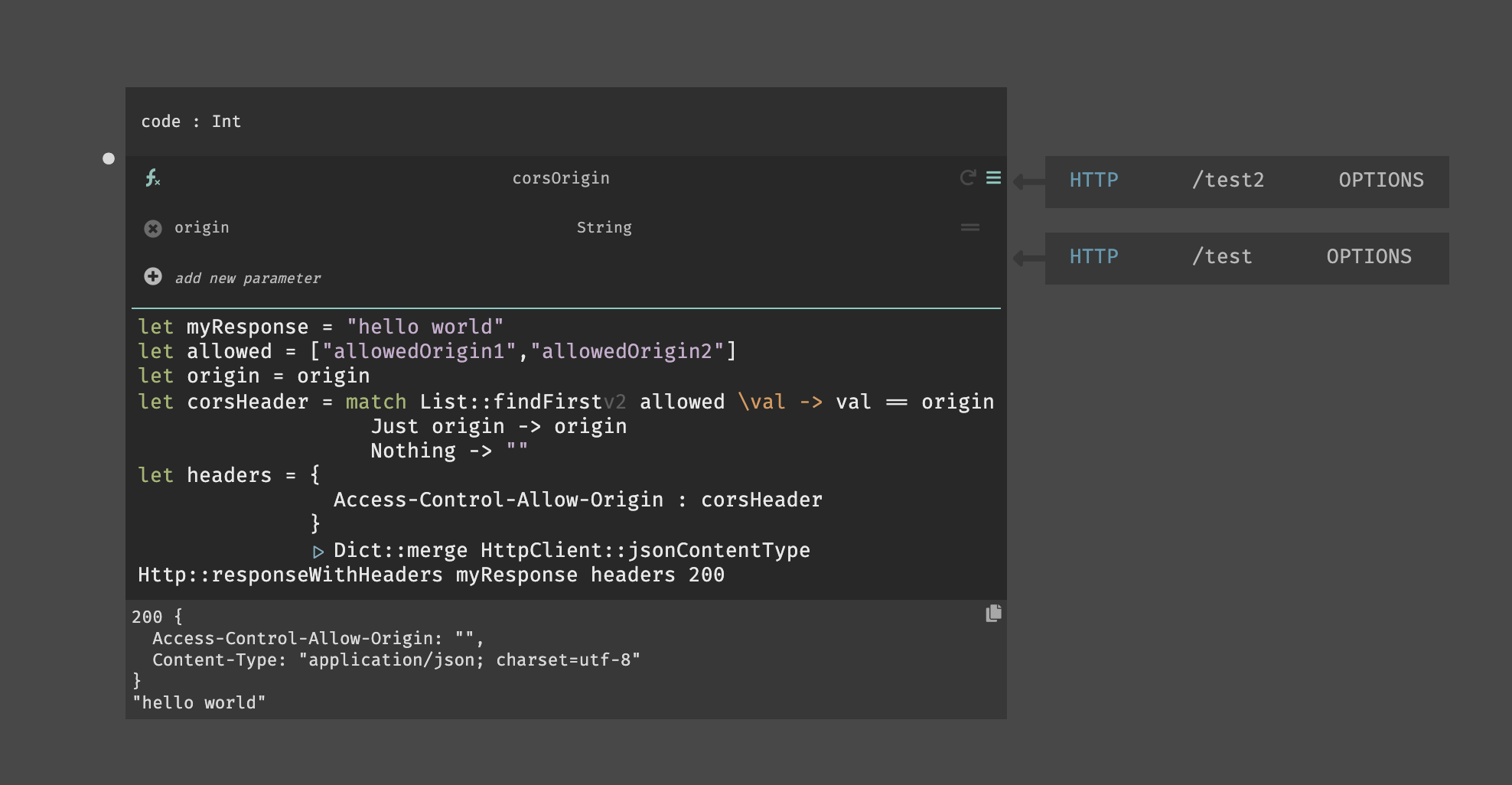
CORS with Custom Domains (Allow-Origin)
As in the simple request above, allowing multiple origins (domains) can be done
in an Options header. You can choose to accept all origins (*) but this will
not allow cookies or auth headers (passing of credentials).
The origin should be passed in the format that it arrives in from the client, in
most cases https://url.comor http://localhost with it's port if you aren't
using 3000, 8000, or 5000, ex http://localhost:8000.
You can set a specific domain directly in the header where we have corsHeader
or if you'd like to check for multiple, you can use a list format as below.
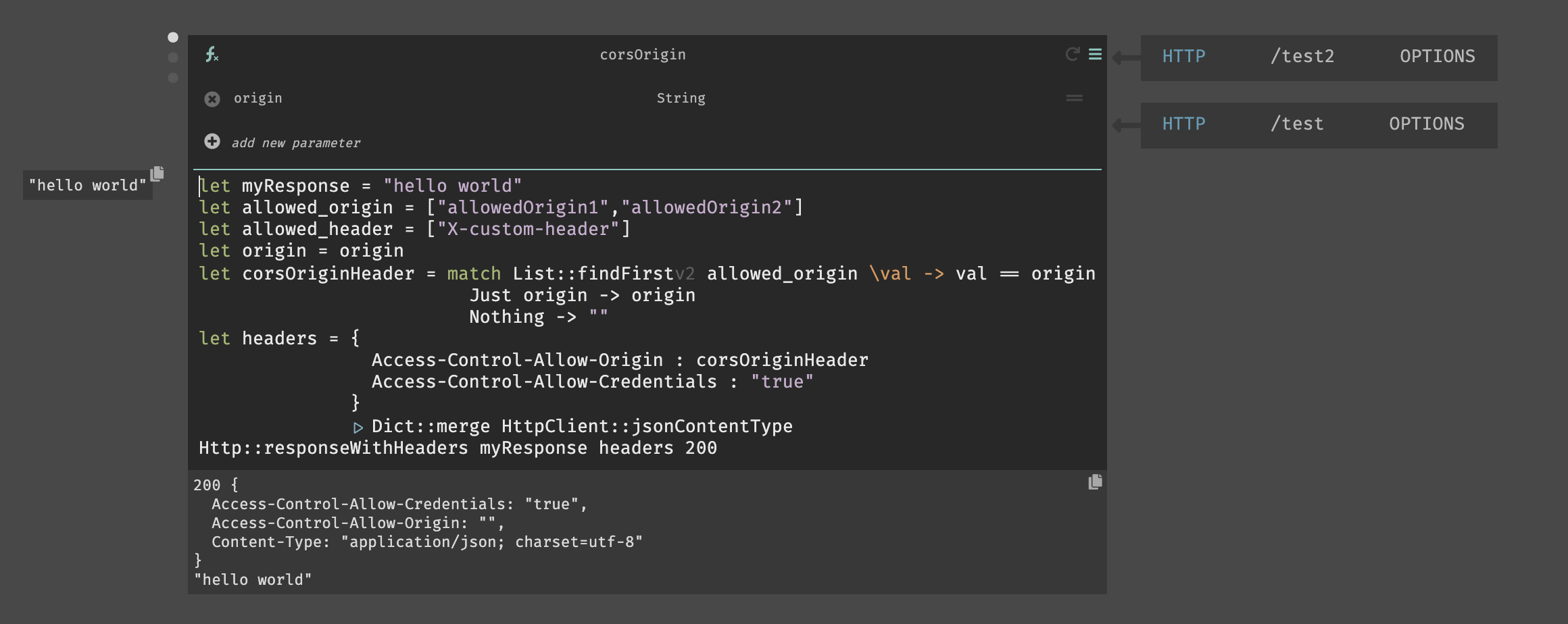
CORS with Authentication (Allow-Credentials)
To allow credentials, add the {Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: "true"}
header to your response. This will not be allowed if the list of allowed origins
is set to *.
CORS with Custom Headers & Methods (Allow-Headers, Allow-Methods)
To allow a custom header, add the:
{Access-Control-Allow-Headers: "headerName"} header to your response.
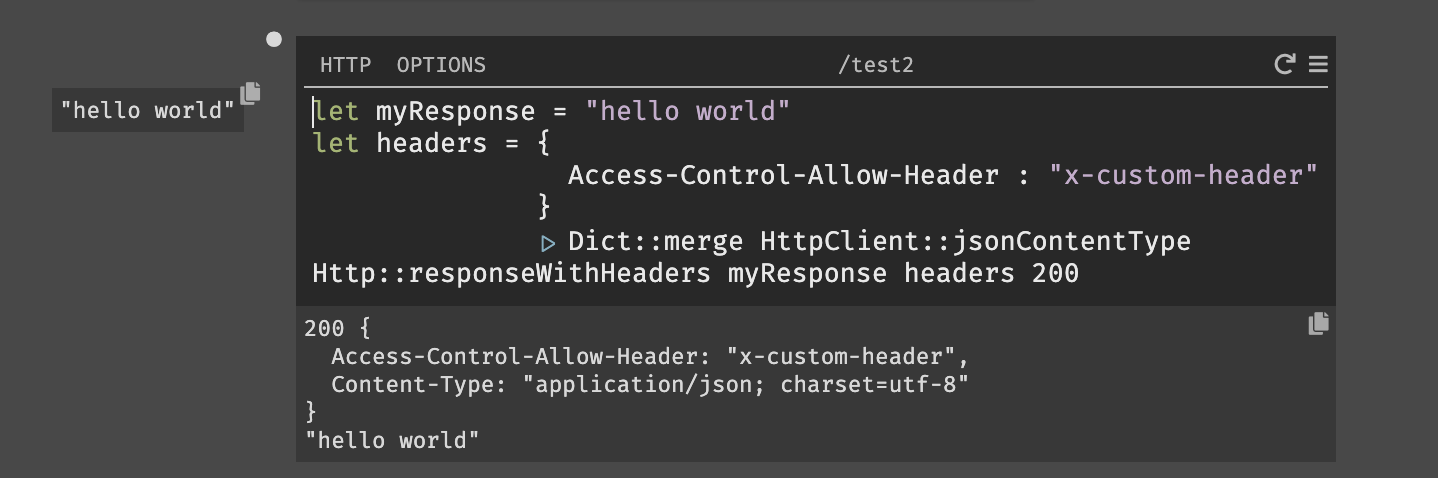
To allow a specific method, add the {Access-Control-Allow-Methods: "method"}
header to your response.
Application Wide CORS
Darklang does not yet have middleware, and preflighting must be added per
endpoint. We recommend creating a function of the logic and then calling it from
each OPTIONS handler.
(Create a function from your Options handler by selecting the code and hitting
Cmd/Ctrl-\ to extract a function).
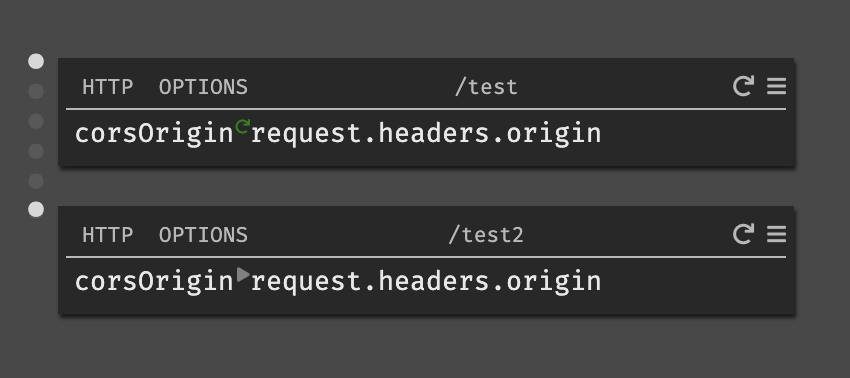
If you are using the same CORS settings for the entire canvas, you could make
one OPTIONS handler for /:url.
Common Errors
"Access to XMLHttpRequest at
https://mydomain.builtwithdark.com/myAPIfrom originhttp://localhost:1022has been blocked by CORS policy: The value of theAccess-Control-Allow-Originheader in the response must not be the wildcard '*' when the request's credentials mode is 'include'. The credentials mode of requests initiated by the XMLHttpRequest is controlled by thewithCredentialsattribute."
This error means that you're trying to make a request from an origin that isn't
explicitly allowed, which means you may not send along cookies. Use
[http://localhost:3000], [http://localhost:5000], or [http://localhost:8000]
when testing your frontend locally. If this is a URL from the internet, use the
documentation for Access-Control-Allow-Origin above.
"Access to XMLHttpRequest at
https://mydomain.builtwithdark.com/myAPIfrom originhttp://localhost:1022has been blocked by CORS policy: The value of theAccess-Control-Allow-Credentialsheader in the response is '' which must be 'true' when the request's credentials mode is 'include'.
This error means that your response needs to include the header
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true.