Tutorial: Create a HTTP handler
Let's start by using the editor to write an API endpoint that responds to a browser HTTP request.
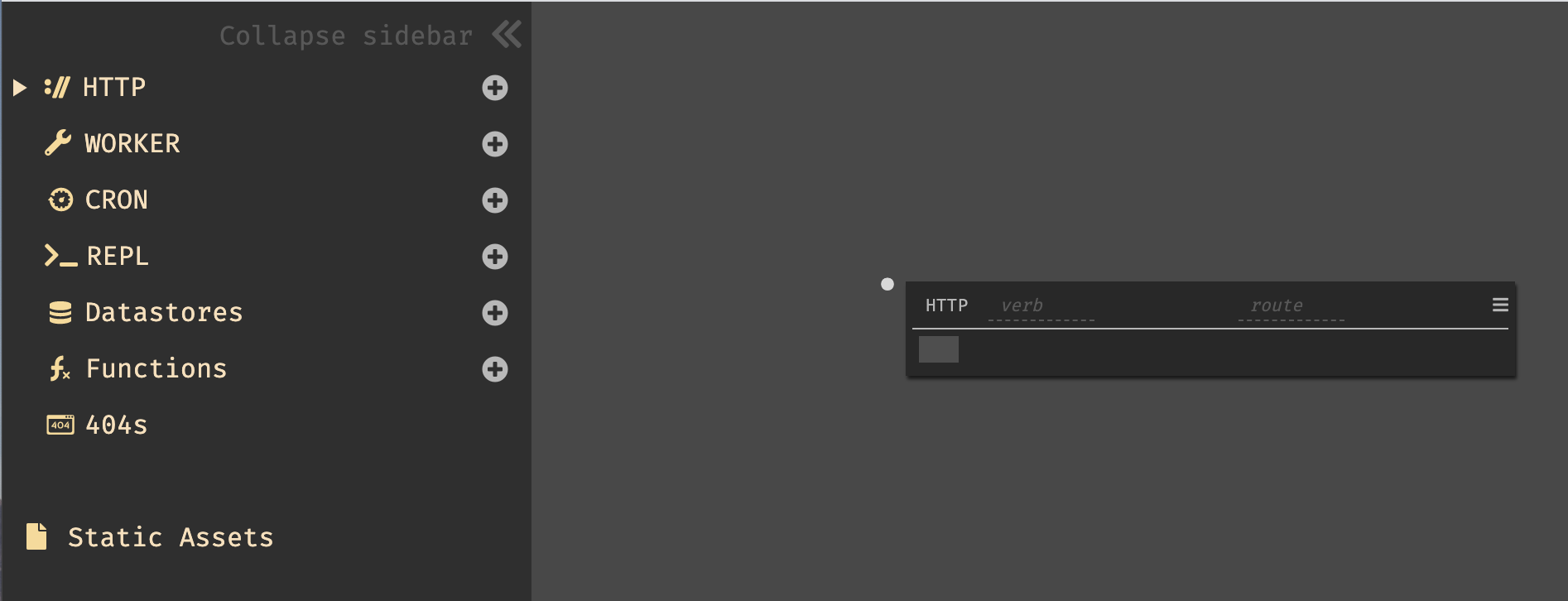
- To create a new HTTP endpoint, we first bring up the omnibox, by clicking
anywhere on the screen, pressing
Cmd-k/Ctrl-k, or pressing the plus next toHTTPon the sidebar.
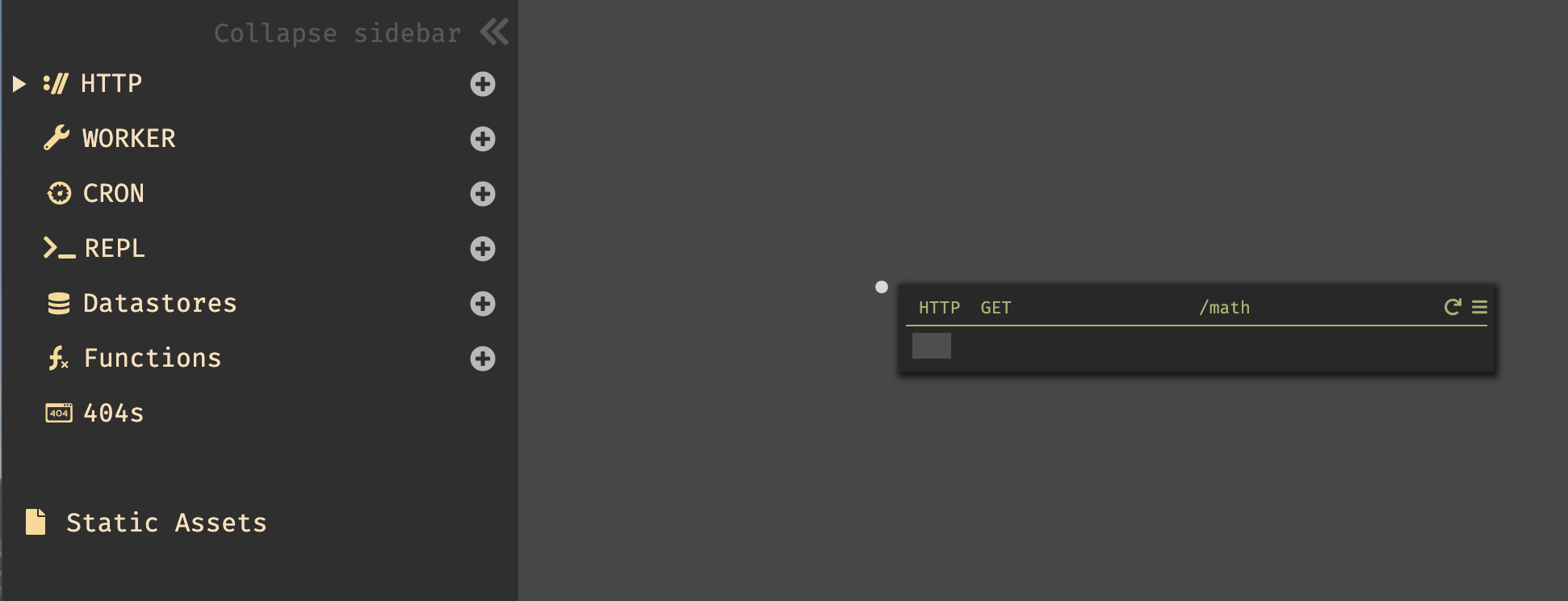
- Enter the HTTP method
GET, and the HTTP route/math.
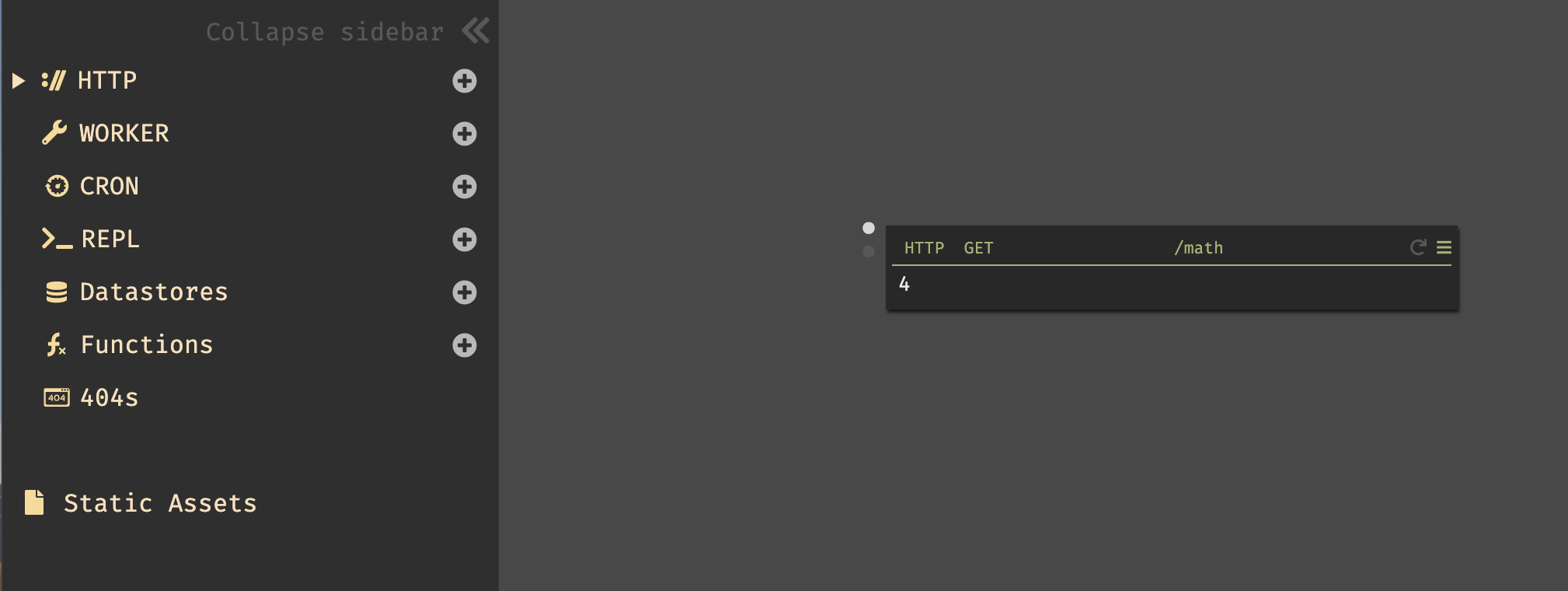
- You can now write any code in the blank – this is the return value of
the API endpoint that you've just created. To start with, let's just return
4.
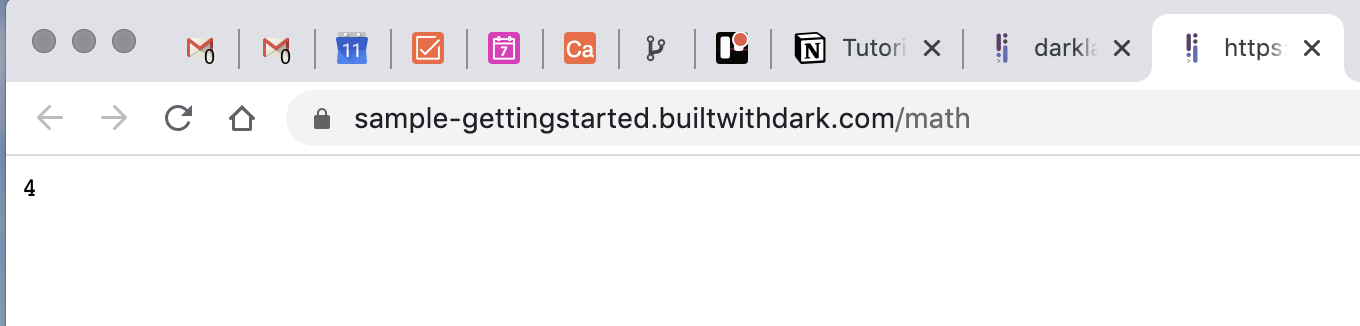
- Click the handler's menu (☰) in the upper right and select "open in new tab", to see your API endpoint running in production.
- Go back to Darklang to edit your code. Add
+ 5to the end of the code and leave your cursor in line.
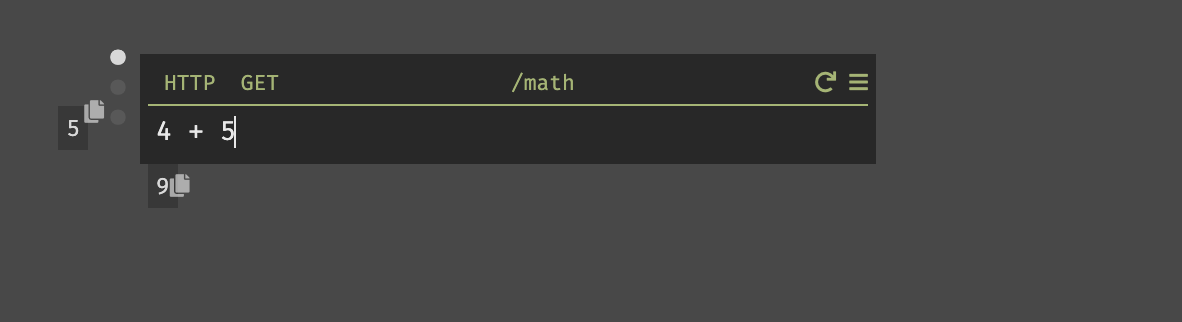
-
The
9below the handler shows you the return value for the handler. -
The
5on the left shows you the result of the expression where the cursor currently is (in this case, 5). This isn't very useful when it's an integer, but if it's a variable it will show you the result of the variable.
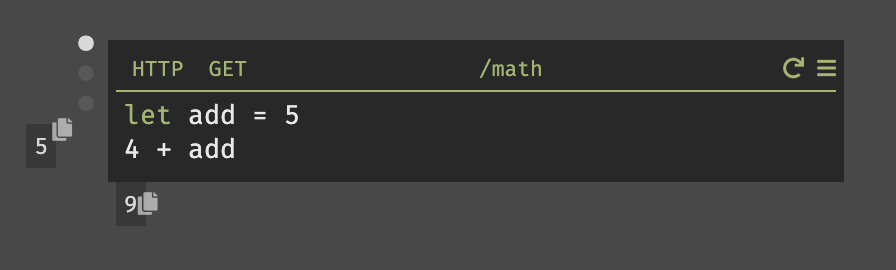
- Hover your mouse over the white dots on the left. Each dot is a "trace", representing a single request to your handler. Traces are fundamental to coding in Darklang, and we'll come back to them later.
Congratulations! You've now created (and deployed) a HTTP endpoint on Darklang.