Using an External DB
Your project may require a more complex data structure than our datastores. If a key-value store works, we strongly recommend using the built-in datastore to take advantage of language functions.
If you already have (or otherwise require) an external database, any external database that provides a REST API can be used. For the purposes of this tutorial, we will be using restdb.io.
Set Up
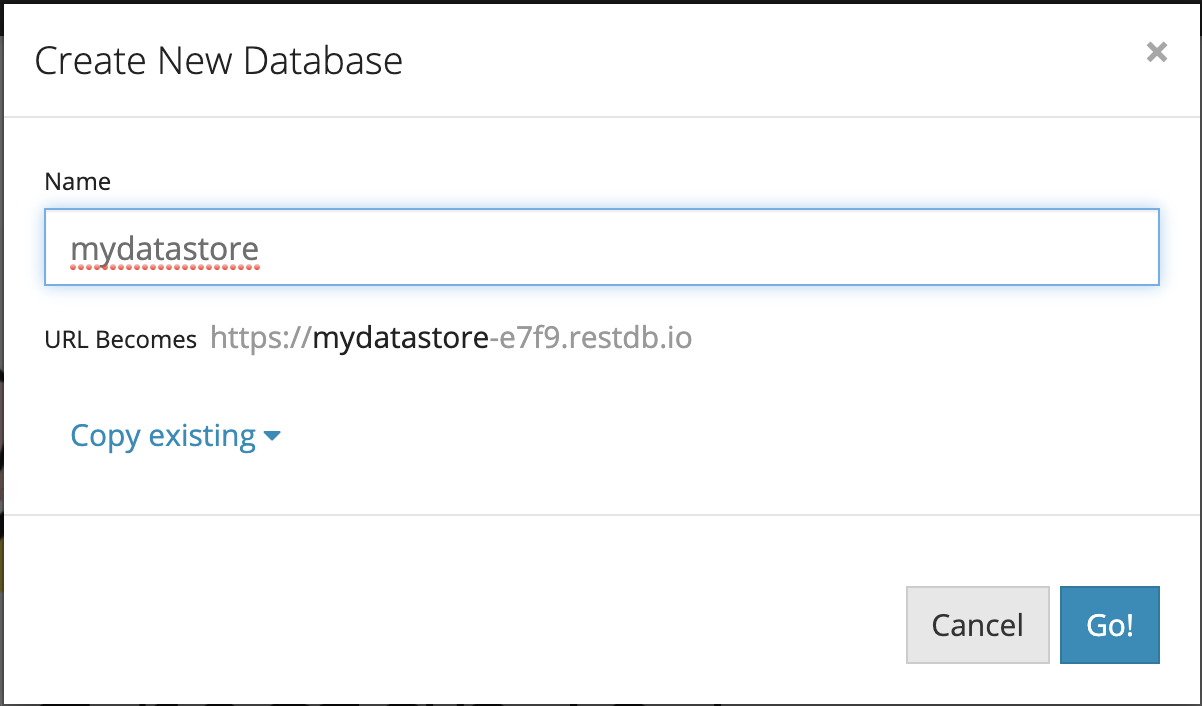
- Create a new database.
- Select Developer Mode in the upper right, and then choose Collections +

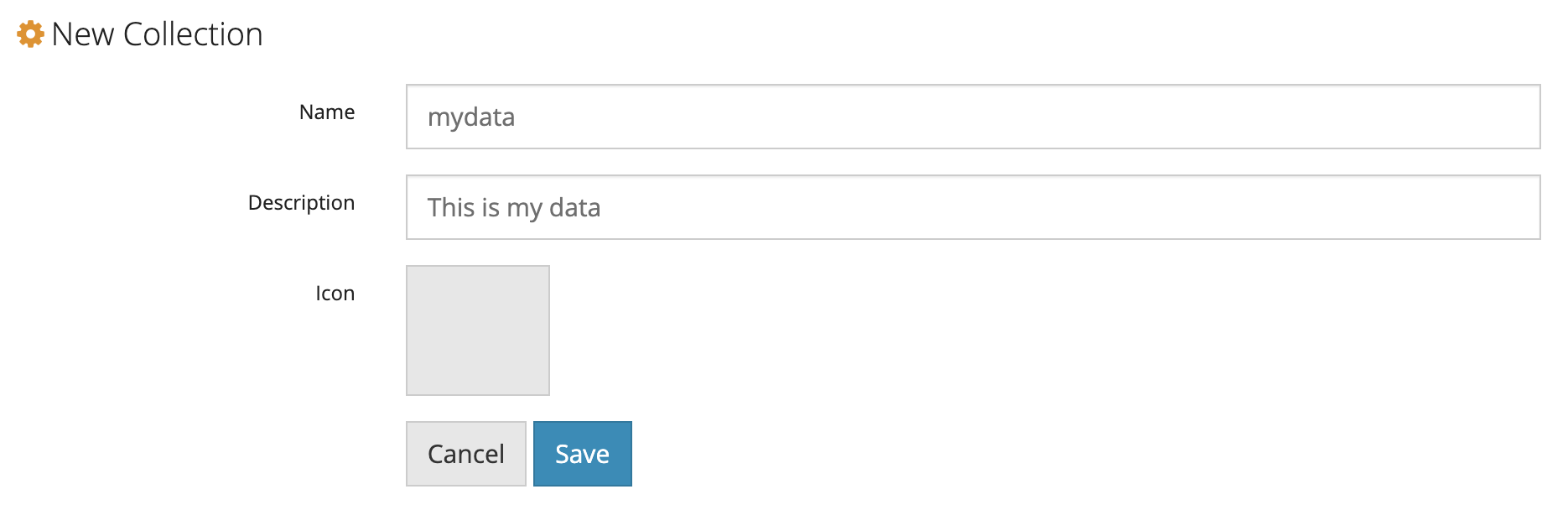
- Enter the information for your new collection and click Save.
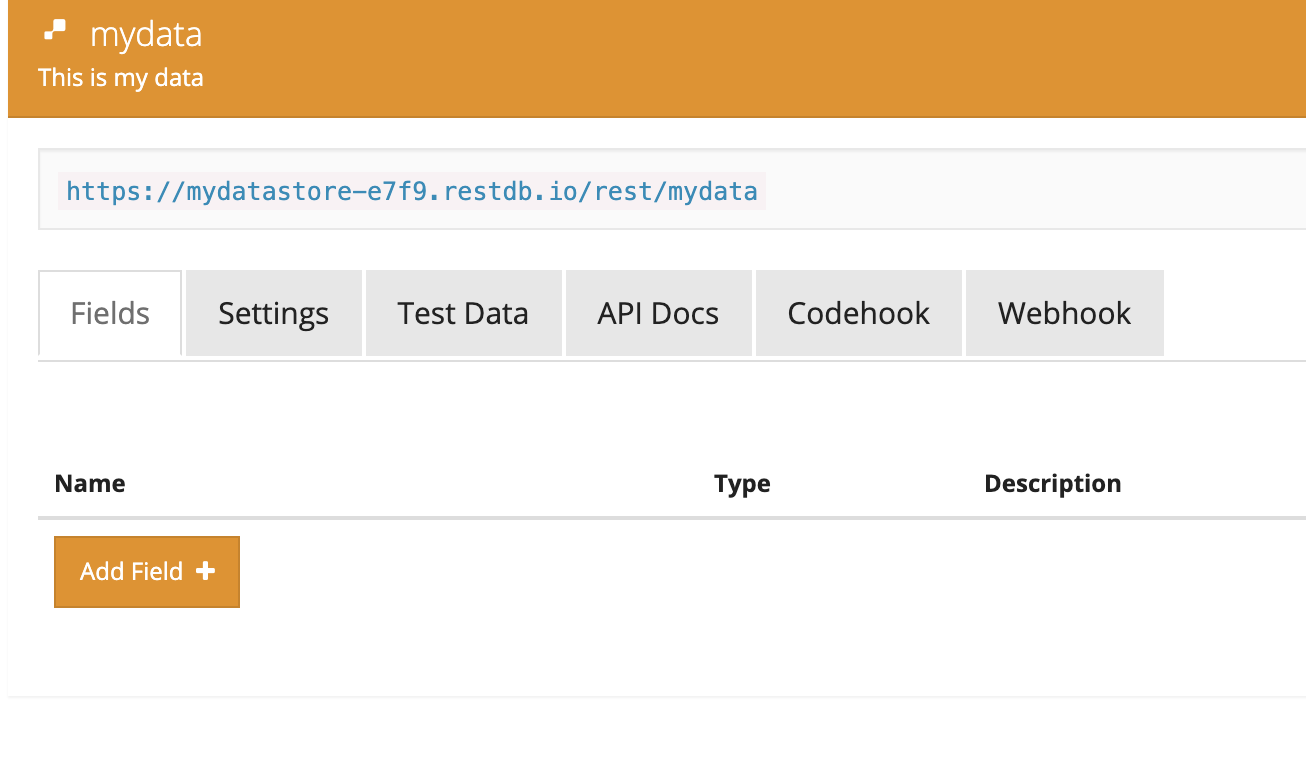
- Add Name and Description text fields to your database by clicking Add Fields +.

-
Grab your API Key by clicking on API Docs and finding the value labeled
x-apikey:. Save it as a function in your Darklang canvas. -
Optionally, also grab the URL at the top of your page (in my case, its
https://mydatastore-e7f9.restdb.io/rest/mydata) and save it as another function in your Darklang canvas.
POST a New Record
-
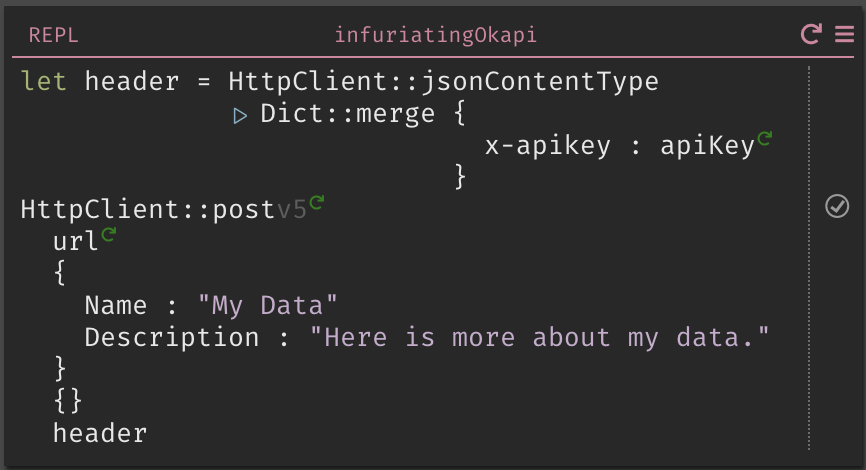
Create your header by doing a
Dict::mergeonHttpClient::jsonContentTypeand a dict containing your API Key -
Write an
HttpClient::postusing your URL, your fields (note: the field names are case sensitive) and your header, and then run it.
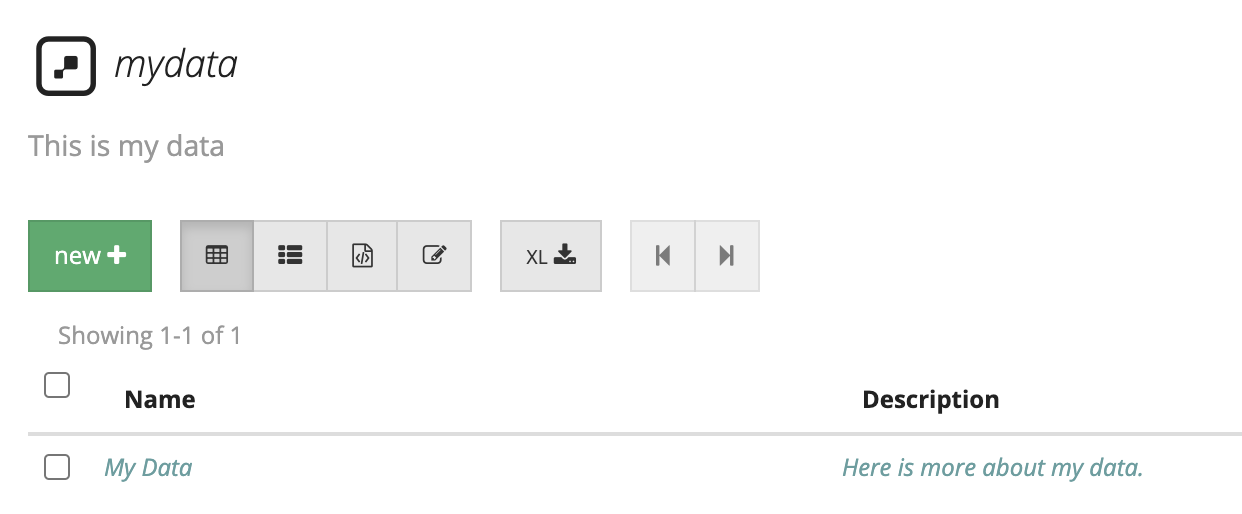
- Your data will appear in the restdb.io console.
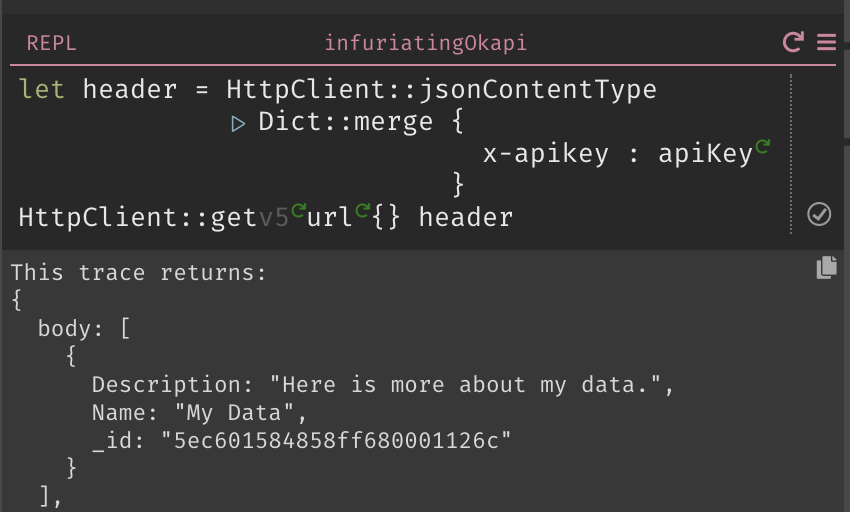
GET All Data
-
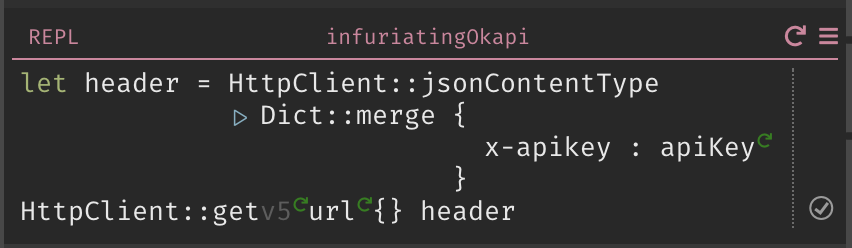
Create your header by doing a
Dict::mergeonHttpClient::jsonContentTypeand a dict containing your API Key. -
Write an
HttpClient::getusing your URL and header, and then run it.
- Your handler will return all of the data in your database.